Do the contents of your head matter? Sorry for asking, of course they do, they are unique and full of the explored and unexplored possibilities. Do you keep an eye on your body? Sorry for asking, of course you do, and that sandwich was wholegrain (maybe).
What about the <head> & <body> section of your site's HTML document? Do its contents influence how your site performs in the eyes of search engines?

Let's collect all the evidence that we have up to date and form a picture of SEO value of HTML tags in 2018.
However, first, there are some definitions, so that we agree that we have the same thing in mind when thinking about HTML tags.
HTML tags are…
…chunks of text that exist in HTML. They are invisible to users (unless they look them up in the page's source code), and they provide data about your page to search engines. Thus, they help search engines understand what your content is about.
They highlight the most important parts of your page to let it stand out in SERPs, which allows users to encounter your content. So, it is natural to assume that HTML tags must be a crucial part of on-page optimization, totally vital for SEO.
It was like that till search engines decided not to always look at tags and get the info on their own.
So,
Do HTML tags still matter in 2018?
It is true that over the previous years, HTML tags' influence on rankings has been decreasing. And now webmasters can even choose not to use some tags in their HTML at all and be ok after that.
However, there are still some tags that:
- Enhance user experience by providing better navigation and best match with queries;
- Give guidance to search engines on where to find the most important parts of the site or which parts to overlook;
- Make SERP snippets look more attractive and informative.
Which tags are those lil' precious helpers, you may ask. Let's talk about each of them in details.
<Head> section.
1. Title tag.
What is this?
Title tags are usually used by search engines to determine the subject of a particular page and display it in SERPs. In HTML a title tag looks like that:
<title>Your Fantastic Title</title>
SEO value
Title tags used to be of huge importance to search engines. A title tag is one of the first things that people see in SERPs. Thus, these tags used to be the ones that got stuffed with keywords up to madness.
Today search engines still understand what a page is about from a title tag. However, with Google's shift to semantic search, the value of a title tag has got somewhat lower. For example, the researchers from Backlinko found that a keyword-optimized title tag was associated with a better ranking, but the correlation was smaller than it once was.
Now the search engine is able to interpret a page's topic without exact keywords in the title but on the basis of all the elements of a page: meta description, images, users' activity metrics, and of course, content itself.
In spite of all this evidence, we can't but agree that title tags are used in three places of the highest visibility:
- SERPs – here is the place where the user decides to click or not to click;
- Web-browser tabs – the visibility in this place is especially important when users have about a million open tabs in their browser (yes, you are not alone);
- Social networks – your title tag is used when the page is shared.
The problem
From time to time, Google chooses not to use your title tag but displays a different one. Pretty annoying, but Google is not the one to force into doing what you want.
There are some reasons why this problem may occur:
- The title is keyword-stuffed — it is obvious to optimize your title for target keywords, however, it is important not to overdo it. Otherwise, Google will rewrite your title in a way it considers proper.
- The title does not match a query — Google may choose your page for a particular query even if your title does not match this query. In this case, the title may be sometimes rewritten for SERP. It is obvious that you cannot write a title that matches all the possible queries. However, if you see that Google rewrites your title for high-volume queries, then consider revising it.
- There are some alternative titles — Facebook and Twitter have their own tags in the <head> section, so if you use the alternative titles for these social networks, Google may also use them instead of your title tag.
How to optimize
I think you should know it. It is really easy to optimize titles! There are some tips on writing the ones that Google will definitely like:
- Title length
It is advisable to keep it under 60 characters long, otherwise it can be cut in SERPs, and some of your important words may be omitted. Plus, keep in mind that letter W occupies more space than, for example, letter I or some lower-case letters.
Thus, if your title is rather long, it is advisable to avoid Caps Lock and count characters keeping in mind how much space they occupy. Remember to use character savers, like the ampersand (&) symbol instead of ‘and', the slash (/) instead of ‘or', etc.
Anyway, a long title is not a mistake, there is no punishment for it. But I'm sure that you would like your titles to be fully seen in search results.
To check on your titles, open your WebSite Auditor's project or create a new one, go to Content Analysis > Page Audit > Content optimization, and analyze the Title section.
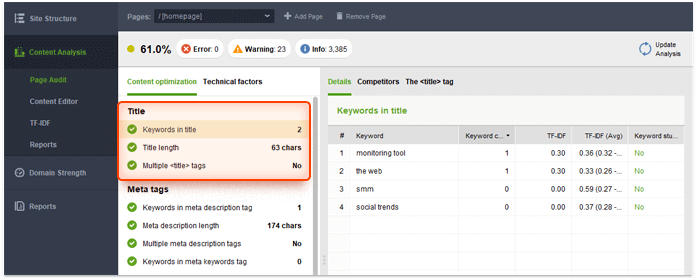
It is also possible to edit your title in-app and see how it will look in SERPs. Go to Content Editor > Titles & Meta tags and make your title look awesome:
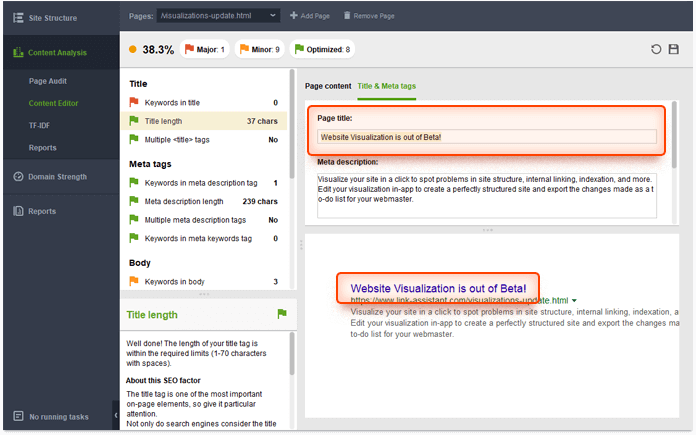
- Title keywords
If you do not want Google to rewrite your titles or punish you for causing poor user experience, please do not stuff your titles with a million keywords.
However, it is still important to optimize titles for target keywords, just do it smart. Try to incorporate one or two keywords to make a descriptive and unique title. Write for your customers. It is clear that you want to attract more visitors, but you surely would like them to stay and convert, not bounce immediately.
Use your keywords closer to the beginning of the title. This way, users who skim search results will notice your prominent information first.
I would also recommend to avoid duplicate titles, as Google may think that you have duplicate content and penalize your website.
- Brand in a title
In case you have a well-known brand, it is a good idea to use it in the title. It will be some kind of endorsement of your content by the quality and recognition associated with your brand. But, remember to use it in the end of the title (unless it is a Homepage or About page that should be naturally more brand-focused), so that unique information would be more visible.
2. Meta description tag.
What is this?
Meta description is a short paragraph of text in the HTML <head> section of a page. It is usually displayed in a SERP snippet after website's title and URL. In HTML it looks like this:
<meta name="description" content="Your gorgeous description">
SEO value
The value of meta description is very close to the title's. It is an important element of a page that helps search engines to determine the subject of the page and allows users to understand whether the page matches their query.
Though meta description is not a ranking factor, it still determines whether the user is going to click on your page thus influencing a click-through rate. Plus, an accurate description that matches your content will significantly reduce a bounce rate.
Meta description can be seen in two places of the highest visibility:
- SERPs — meta description occupies the largest part of a SERP snippet;
- Social networks — meta description usually appears when people share your URL across social media channels.
The problem
Similar to the deliberate use of titles by Google, the description displayed in SERPs may differ from the one that you specified in the <head> section.
It appears that meta descriptions are even more query-dependent than titles. In one of the hangout sessions, John Mueller mentioned that they were adjusting the description on the basis of the user's query.
As a rule, Google uses the description specified in the <head>, but when there is a need for more information or more context to match the query, it can take some parts of the content as well. This is actually a reason why the search engine has started to display longer snippets.
There are none few ways to tweak this problem, as you cannot possibly write the description to match all the queries. The most perfect thing you can do is write the description that matches best your page's content.
How to optimize
- Meta description length
Not so long ago, to be fully displayed in a SERP snippet, the meta description length had to be about 160 characters. Then gradually this value increased up to 300 characters. Finally, on December 2017, the snippets passed the 300-character mark.
What should you do in this situation? Many people ran some experiments to understand what the safe length for meta description is. Well, the answer to this quest — there is no safe length.
First of all, the description of any length is allowed. If it is too long, Google will cut it, but it is not a catastrophe. I think the safest way is still stick to ~300 characters and keep an eye on the latest findings on this subject.
You can check out your meta descriptions in WebSite Auditor. In your project, go to Content Analysis > Page Audit > Content optimization, and analyze the Meta tags section.

It is also possible to edit your description in-app and see how it will look in SERPs. Go to Content Editor > Titles & Meta tags and experiment with your description:
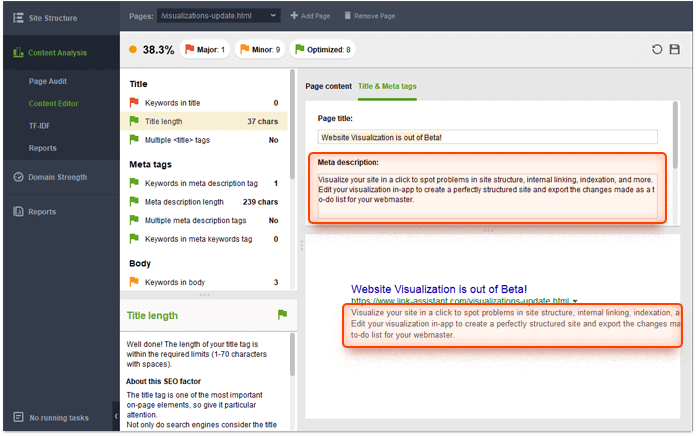
- Meta description as an ad for your page
In the situation when Google plays around with your descriptions matching users' queries, why not create a description for users? Try to make such a description that advertises your page's content in a best and concise way possible. And avoid duplicate descriptions — search engines may think that you have duplicate content on your website.
Plus, remember that search engines bold query's keywords in the descriptions. Such bolded words draw users' attention. So, optimizing your meta description for target keywords is still quite important.
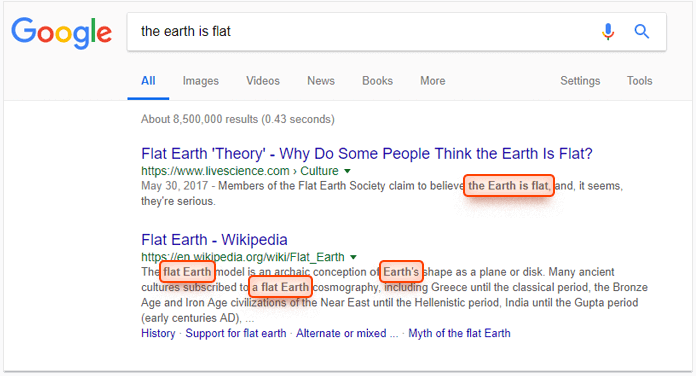
- No quotation marks in meta description
When you use double quotation marks in the HTML of meta description, Google will cut this text at the quotation mark when displaying it in SERPs. Thus, it is better to remove all the alphanumeric characters from your meta descriptions.
- Schema markup
No kidding, you can actually make your SERP snippet rich. By using a special markup, you can add elements to your HTML that will make your snippets look more appealing to users. For example, they can be adorned with star ratings, customer ratings, images, additional product information, etc.
Thanks to Google, you don't have to be a web developer if you need to mark up the structured data on a website. You can use Structured Data Markup Helper. Before adding the schema markup chunk of HTML to your pages, remember to preview your snippets by copying and pasting your page's source code into Google's Testing Tool.
3. Open Graph tags.
What is this?
Open Graph (OG) tags are additional meta tags in HTML <head> section of a page that allow any webpage to become a rich object in social networks. It was first introduced by Facebook in 2010 and further recognized by other major social media platforms (LinkedIn, Google+, etc.)
In HTML it can look like this:
<meta name="og:title" property="og:title" content="Your Awesome Open Graph Title">
SEO value
OG tags let you control how the information about your page is represented when shared via social channels. This possibility may help you enhance the performance of your links on social media, thus driving more click-throughs and increasing conversions.
How to optimize
Before you decide to implement OG tags to your HTML, consider some optimizing. There are quite a few Open Graph tags, I will give a few tips on the most important and popular ones.
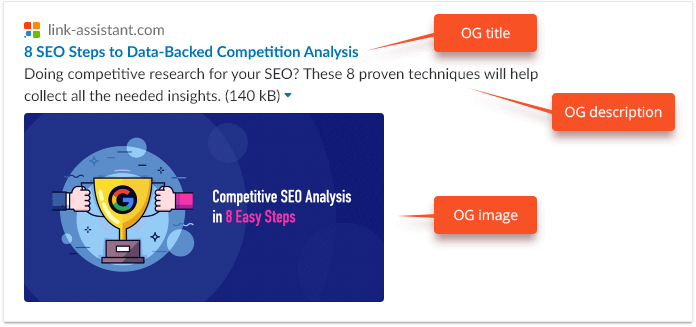
- OG title
It is clear, here you specify your content's title. You can copy-paste your title tag if you think that it is compelling enough for social media channels.
Keep in mind that it should be between 60-90 characters, otherwise, it may be truncated.
- OG type
With the help of this tag, you can describe what kind of object you are ready to share: a website, post, video, company, etc. You can check the complete list here.
This tag is considered important when your page has the Like button. It may help to determine whether your content will appear in the Facebook user's interest section in case she or he "Likes" it.
In most cases, the type is "website", because you mostly share links to websites. If so, you do not need to specify the type in the code, it will be read as such by default.
- OG description
This one is very similar to the meta description tag. However, it won't be displayed in SERPs, it will be shown as the summary when your page is shared. For this reason, there is no point in craftily sneaking your keywords into this particular description.
Your main task here is to make it speak to your potential audience and drive more clicks.
As for the length, it is considered to be a good practice to keep it about 200 characters.
- OG image
This is a real ace up your sleeve. An image will make your shareable link 500% more attractive. So give it your best shot.
It is clear that the image should catch an eye, call for suitable associations. You can place some text upon your OG image to either reiterate the main point of your content or call to any action. Just try to place text (or the most significant part of it) in the middle of an image, as for example, Facebook likes to trim the sides of thumbnails.
The recommended resolution for the OG image is 1200x627 pixels, the size — up to 5MB.
Once you are done with your OG meta tags, you can check how everything looks like with the help of Open Graph Object Debugger, a tool created by Facebook.
- Twitter cards
Twitter cards are very similar to OG tags (title, description, image, etc.), but they are used exclusively by Twitter. Though now tweets can exceed historic 140 characters, these cards are a nice extension that allows your tweet to stand out in the crowd of common text tweets.
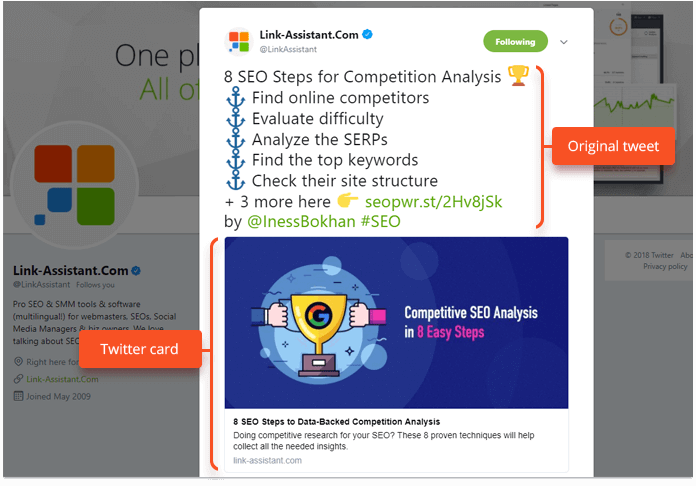
There are a few types of twitter cards out there:
- Summary card - apart from the original tweet, there is a preview of your page's content, which is good for highlighting blog posts, products, news, etc. Title: 70 chars
Description: 200 chars
Image: 120x120px, up to 1MB - Summary card with a large image — this card is similar to the previous one, but it contains a larger image. The image can also include some text that conveys the main point of your page's content, a call to action, or something really provoking to click. Title: 70 chars
Description: 200 chars
Image: 280x150px, up to 1MB - Player cards — such cards enable users to play videos or audios within a tweet. Description: 200 chars
Video: H.264, baseline profile, level 3.0, up to 640 x 480 pixels at 30fps.
Audio: AAC, Low Complexity Profile - App cards — such cards enable users to download mobile apps right from a tweet. They feature a name, a description, an icon, a rating, and a price. Title: rendered from app ID
Description: 200 chars
Image: rendered from app ID
Note: Only one card-type per page is supported.
Once you are ready with your Twitter card's elements, you have to do two things:
- Set up the cards for your pages. Start here.
- Validate your cards here. The validator tool will let you check whether there are any errors and let you preview your cards.
Player cards need to be additionally approved by Twitter. Use this guide to find out how to do it.
4. Robots tag.
What is this?
A robots tag is an element in the HTML of a page that informs search engines which pages on your site should be indexed and which should not. Its functions are similar to robots.txt's. But it is generally used to prevent search engines from indexing individual pages, while robots.txt prevents them from indexing a whole site or any its part.
In HTML it can look like this:
<meta name="robots" content="index, follow">
SEO value
It is not that a robots tag may help you boost your rankings, but you can use it to save your rankings in case you have to block some pages from indexing.
For example, you can have some pages with rather thin content that you are not interested in being indexed in search, but which you would like to keep. In this case, you can just add a noindex tag for this page.
How to optimize
- Correct use of a robots tag
If you do not add this tag to your HTML, search engines will crawl and index all your pages by default. It only makes sense to use a robots tag if you want to change any of these parameters.
Plus, if any page is in the section that is disallowed from crawling by a robots.txt file, then any robots tag in HTML of this page will be ignored.
- Correct use of robots tag's parameters
Google understands and respects the following parameters that you can specify in your robots tag:
- Noindex — prevents search engines from indexing a page;
- Nofollow — prevents the search engine from following ALL the links on the page (that's why it is different from the nofollow attribute that is applied on an individual URL level);
- Noarchive — prevents a cached copy of the page to appear in search results;
- Nosnippet — prevents a description of the page to appear in search results as well as prevents caching of the page;
- None — the same as "noindex, nofollow".
Note that Google understands any combinations of lowercase and uppercase that you use for your robots tag parameters.
- Robots tag and safety
Beware that malicious crawlers may ignore all your robots tag's parameters, so if you use them as a measure of security, it won't do you any good.
If you have any private information that you would like to keep from public, opt for a more secure approach, like password protection, for example.
5. Canonical tag.
What is this?
When you have a few pages with identical content, you can use a canonical tag to tell search engines which page should be prioritized.
In HTML it may look like this:
<link href="URL" rel="canonical">
SEO value
A canonical tag is important for SEO in two ways.
First of all, it not only tells search engines which page out of a few similar ones is more important, it also shows them that such pages are not duplicate content. As duplicate content is punished by death penalized, this tag is a killer feature.
Second, it prevents cannibalization that happens when pages that are less important than other similar ones get higher rankings.
How to optimize
Open your WebSite Auditor's project, go to Site Structure > Site Audit, and pay attention to the On-page section, namely to Duplicate titles and Duplicate meta descriptions.
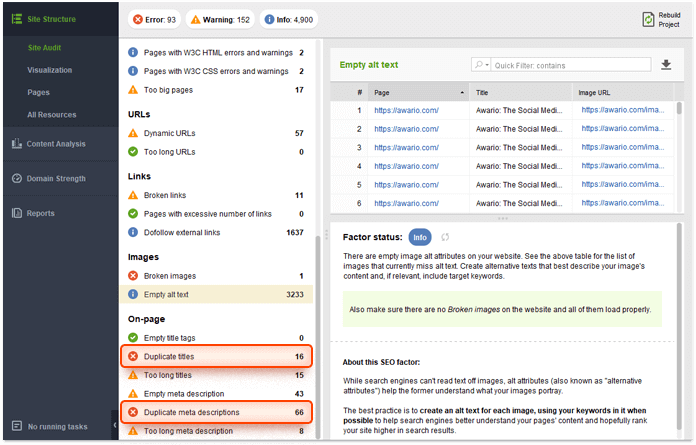
In case you have a few URLs with identical content, specify a <link rel="canonical"> element in the page's HTML.
<Body> section.
6. Header tags.
What is this?
Header tags are the headings (h1-h6) you use to structure your page. In HTML a header tag may look like this:
<h1>Your irresistibly appealing heading</h1>
SEO value
It is no secret — it is totally ok not to use header tags at all. Everything will surely be fine. However, these tags help search engines read your content in a more efficient way. The order of your header tags (h1 to h6) shows the level of importance of each section.
What's more, when a page is level-structured, it is much easier for visitors to read it and comprehend the most important parts in a short amount of time.
Plus, from time to time, Google likes to make list-type featured snippets out of the headings of a particular page (it usually works for guides and instructions). The h1 of your page will match the query, and your subheadings (h2, for example) will make a chronological list in a featured snippet. The result will be displayed similar to this:
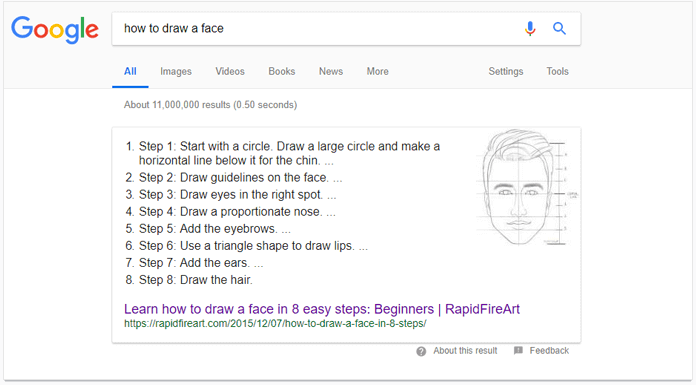
As you may remember, a featured snippet occupies the position above all the results. It is a nice and free opportunity for better visibility.
How to optimize
- Hierarchical order of headings
The hierarchy of your headings will let search engines comprehend your content better. As you know, now they take all the factors into consideration to give the best matching answers to our queries.
It is considered to be a good practice to use one h1 per page and further break up your content logically into sections with h2. If necessary, you can further segment h2 sections with h3, h4, and so on. Just do not stuff your page with an array of different headings. Use them strategically to introduce the main point of each section.
Keep in mind, while the usage of one h1 per page made a real SEO difference before HTML5's popularity, now it is possible to use a few h1 tags per page. As a result, now the importance of these tags as well as of the whole header tag hierarchy has lessened.
- Keyword-optimized headings
As your headings introduce main points of each section of the page, it is a good idea to include your target keywords and their synonyms into them. Moreover, usually your h1 (if you use it once as a page's title) will be similar to your title tag in HTML. Thus, it will be already optimized in line with the title tag.
No keyword-stuffing though! Go for a nice long-tail keyword.
To check your headings for keywords, open your WebSite Auditor's project, go to Content Analysis > Page Audit > Content optimization, and analyze the Body section:

- Visible headings
While search engines read your meta tags, your visitors read text. Thus, you have to not only enhance the indexing of your content but also user experience.
When you use h1 as the title of your page, try to make it visible to visitors, as most likely, this h1 conveys the main topic of your page's content. Thus, it should be:
- bigger than all the other text elements of your page;
- noticeable at one glance: use different formatting and styling elements to make it stand out.
7. Alt attribute.
What is this?
The alt text attribute is a part of an image tag, and it provides a description for an image. In HTML it may look like this:
<img src="url" alt="Your clear-cut image description">
SEO value
Alt text plays a major role in image optimization. It makes your images accessible both to search engines (by telling them what a particular image means) and to people (by displaying an alternative text in case a particular image cannot be loaded or helping screen readers convey images).
How to optimize
- Empty alt texts
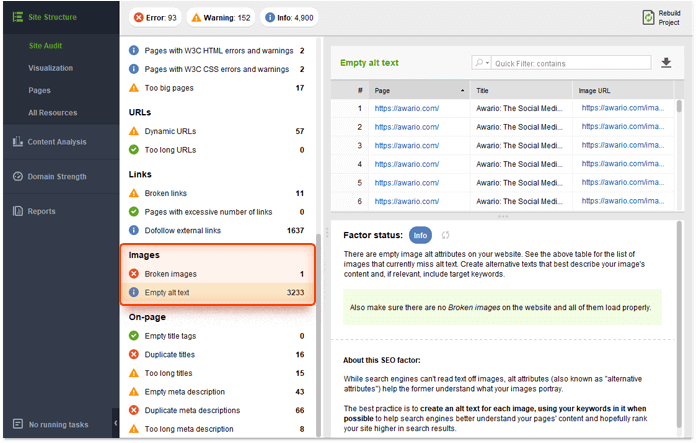
If you want to use this additional opportunity to rank higher by means of image optimization, then first of all, check for empty alt texts. This is where you miss this opportunity whatsoever.
Open your WebSite Auditor project, go to Site Structure > Site Audit, and pay attention to the Images section.
- Useful images
Attention, if you have thousands of images, you do not have to optimize each one (PHEW!). Pay attention mostly to those that convey some useful data, not the ones that are used just for entertainment and decoration.
The useful images are images of products, screenshots of some processes, your logo, infographics, diagrams, etc.
- Keyword-optimized alt texts
Yes, I think, you've guessed, alt texts are one more opportunity to use your target keywords. And you know the drill — do not overuse them! Write the description that provides context to your content and use a keyword where it is suitable. Keyword-optimized images will work great in combination of the factors that search engines take into account when ranking pages.
Plus, try to keep your descriptions rather short — about 125 characters, as screen readers will cut off alt texts at around this mark.
Source:- https://www.link-assistant.com/news/html-meta-tags-for-seo.html







- Follow Us on Twitter!
- "Join Us on Facebook!
- RSS
Contact